Economics eNotes For B.Com/BA/M.com Entrance Exam 200
Father of economics or father of modern economics:- ADAM SMITH
(He is the major supporter of Laissez faire economic policies)
His books are:-
- THE THEORY OF MORAL SENTIMENTS-1753
- AN ENQUIERY INTO THE NATURE AND CAUSES OF WEALTH OF NATION-1776
- Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, business, governments and entire society make when they cope up with scarcity and incentives that influence and reconcile those choices.
- The word economics is derived from the Greek words OKIOS NEMEIN means household management.
Study of economics
MICRO ECONOMICS
FATHER: ADAM SMITH
(Study at individual level)
MACRO ECONOMICS
FATHER: J.M. KEYNES
(Study of aggregate level)
RAGNER FRISCH divided the term economics in two parts- Micro and Macro economics
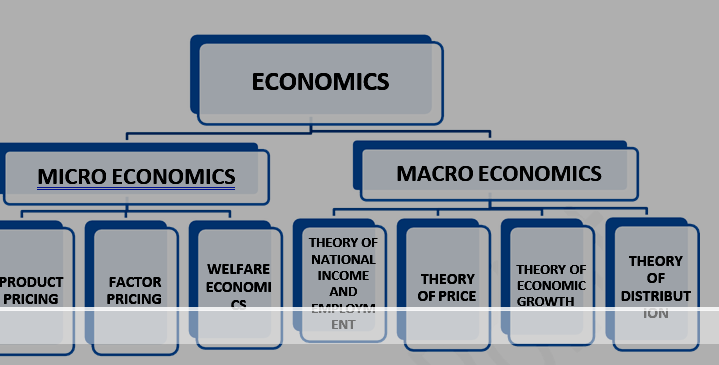
Product pricing: –
Theory of demand and consumer behavior.
Theory of supply and producer behavior
Factor pricing: – Wages, Rent, Interest, Profit
Welfare economics: – what to produce
How to produce
By whom to produce What to produce for whom to producE
Theory of national income and employment:-
Theory of consumption
Theory of investment
Theory of price: – Money supply
Demand for money
Theory of distribution: – Balance of payment, open economy
UTILITY:–
- Want satisfying power of any commodity is called utility. A commodity may have utility but it may not be good to the consumer.
- For example- alcohol has utility to the drinker but it injurious to health.
- Related to psychological concept.
- Utility is different from person to person, place to place and time to time of the same commodity.
- It may be positive or negative.
MEASUREMENT OF UTILITY:-
- Cardinal utility
- Ordinal utility
CARDINAL UTILITY:-
- Given by Marshall
- Utility can be measured in term of utile
- It is quantitative approach
- Law of diminishing marginal utility
- Law of equi marginal utility
- Marshellian analysis
- Subjective or personal
ORDINAL UTILITY:-
- Given by J.R Hicks and Allen
- Utility can be measured by using a ranking system
- It is qualitative approach
- Indifference curve analysis, budget line
- More realistic and better than cardinal utility
- Based on introspection
TYPE OF UTILITY:-
- Total utility
- Marginal utility
- Total utility: – Utility derived from consuming all the units.
𝑻𝑼 = ∑𝑴𝑼 , (TU= always positive)

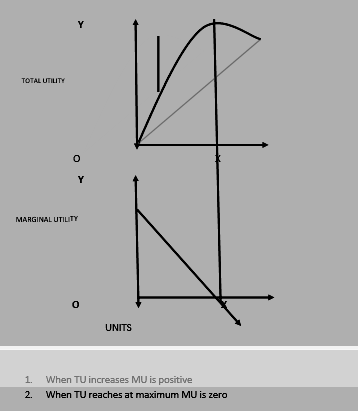
- When TU decreases MU will be negative
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- This law is also known as First law of Gossen.
- This law us scientifically popularized by- Prof. Marshall
- The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as a consumer consumes more and more units of a specific commodity, utility from the successive units goes on diminishing.
Assumptions or conditions:
- Homogeneous commodity
- Fixed place and time of consumption
- No change in the value of commodity
- No change in the value of substitute goods
- No change in income, taste, fashion of consumer
- Standard size of commodity
Criticism or exception:
- Miser man
- Initial stage
- Drunker
- Very small units
- Various use of commodity
- Intoxicant
- Music, good poem, beautiful seen etc.
Law of equi marginal utility:-
- This law is also known as Second law of Gossen, law of substitution, law of maximum satisfaction, law of economy, law of maximum consumption.
- According to this, a consumer is in equilibrium when he distributes its given income among various goods in such a way that marginal utility derived from the last rupee spent on each good is the same.
Assumptions:
- Rational consumer
- Marginal utility of money is same
- Expenses are made in small units
- Time and place should be same
- Income, fashion, interest etc should be unchanged.
Consumer Equilibrium: – Consumer equilibrium is a situation when h given income on the purchase of one and more commodities in such a way that he m gets maximum satisfaction.
- In case of one commodity:-
𝐌𝐔𝐱 = 𝐏𝐱
- In case of more than one commodity:-
- In case of more than one commodity:-
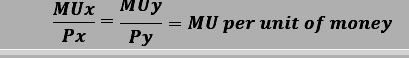
Ordinal approach:-
It is also known as Ordinal utility analysis, Indifference curve analysis, and Equal satisfaction utility curve.
Founded by- Hicks, Allen and Parato
The concept of indifference curve is originated by- Edge worth in 1881.
- Indifference curve analysis:-
Originally developed by an Italian economist Pareto and subsequently it came in fully developed form by the British economist J.R Hicks and R.G.D Allen.
An Improvement over cardinal approach
IC is based on the idea of ordinal utility and scale of preference.Indifference curve: – An IC refers to a curve that shows various combinations of two goods which give equal amount of satisfaction to consumer
| Combination | X | Y | MRS |
| A | 1 | 10 | _ |
| B | 2 | 7 | 1:3 |
| C | 3 | 5 | 1:2 |
| D | 4 | 4 | 1:1 |



- Price of commodity
- Income of consumer
- Price of related goods
- Taste and expectation of consumer
- Consumer preference
- Consumer credit facilities
- Size and composition of population
- Distribution of income
- Government policy
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INCOME AND DEMAND OF CONSUMER FOR DIFFERENT GOODS:
- Normal goods: positive relation (income increase, demand increase)
- Giffin goods: negative relation (income increase, demand decrease)
- Inexpensive goods: no effect of income on demand (needle, match box)
PRICE RELATED GOODS:
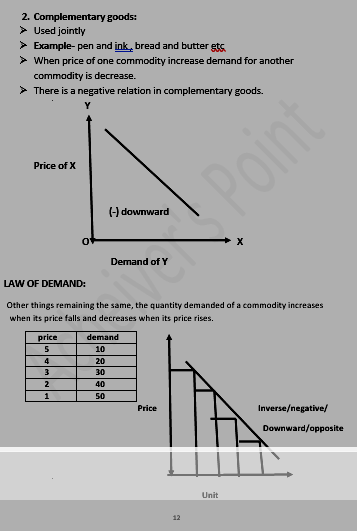
- Substitute goods:
- used in place of one another
- Example- tea and coffee, Pepsi and coca cola
- When price of one commodity is increase then demand of another commodity is also increase.
- There is a positive relation in substitute goods.

- Other things remaining the same- Ceteris Paribus
WHY DOES DEMAND CURVE SLOP DOWNWARD FROM LEFT TO RIGHT?
- law of diminishing marginal utility
- income effect
- substitution effect
- increase in number of consumer
- several uses of commodity
EXCEPTIONS OF LAW OF DEMAND:-
- Giffin goods
- Article of snob appeal (desire to own unique product)/conspicuous consumption
- Veblen effect (luxury goods)
- Emergency
- Quality price relationship
- Ignorance
- Future price change
GIFFIN GOODS OR GIFFIN PARADOX:-
- Introduced by Sir Robert giffin, Scottish journalist and statistician
- Opposite of law of demand
- Giffin goods are inferior goods
- When the price of giffin goods falls, the poor will buy less and vice-versa

ELASTICITY OF DEMAND:-
- Degree or magnitude of change in demand due to change in price, income, price of other commodity etc
- LAW OF DEMAND- study the change in direction
- ELASTICITY OF DEMAND- study the change in direction and change in degree
TYPE OF ELASTICITY:-
- ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (Ed)
- Price
- Cross
- Income
- Advertising
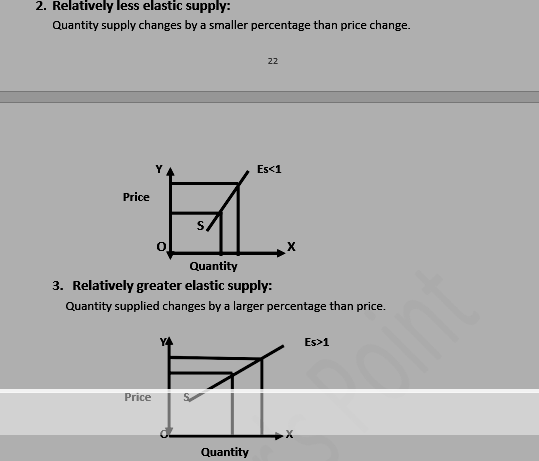
2. ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY (Es)
- Price
- Cross
v Price elasticity of demand= %change in demand / %change in price
- Income elasticity of demand= %change in demand / %change in income
v Cross elasticity of demand= %change in demand of x / %change in price of y
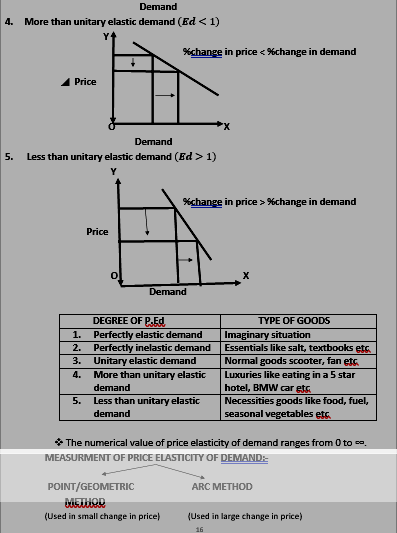
DEGREE OF PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND:-
- Perfectly elastic demand
- Perfectly inelastic demand
- Unitary elastic demand
- More than unitary elastic demand
- Less than unitary elastic demand











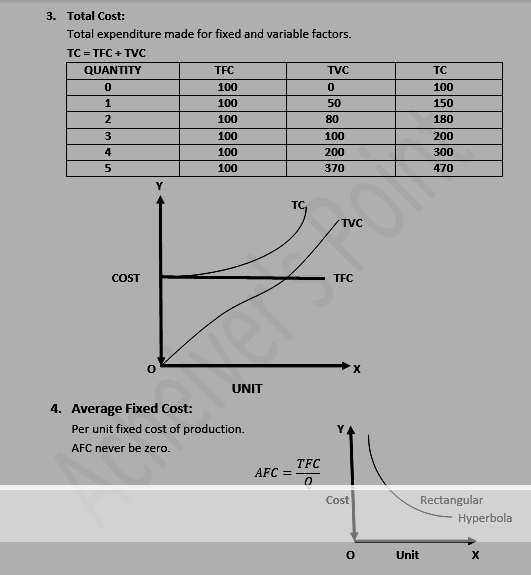

A. Accounting cost:
Ø It is also known as explicit cost.
Ø This cost is actually incurred and recorded in the books of account.
Ø Payment made by producer for external factors.
B. Economic cost:
Ø It is wider and involves accounting cost.
Ø Economic cost also includes explicit cost, implicit cost and normal profit.
C. Sunk cost:
Ø The cost remains unchanged all level of activity.
Ø Ex- depreciation, loan, rent of building etc
D. Shutdown cost:
Ø Cost incurred by a firm when it temporally discontinues its operation.
E. Opportunity cost:
Ø It was first used in 1894 by David.L.Green.
- It is also known as alternative cost, transfer earning, and cost of alternative foregone, transfer price.
- It does not recorded in book of accounts.
- Opportunity cost is the cost of next best alternative.

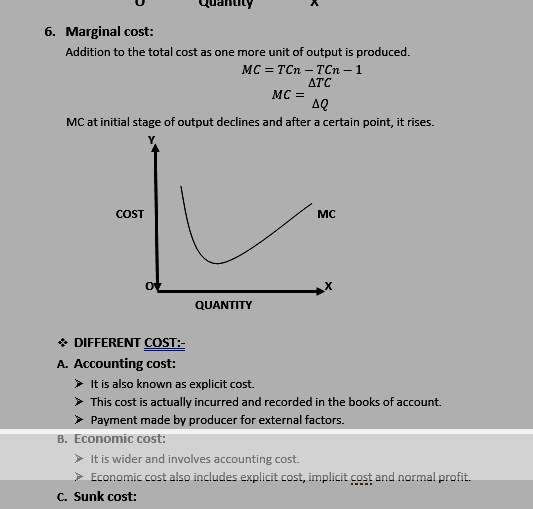
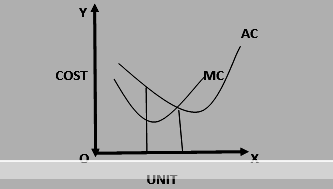
v RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN AC AND MC:-
- If AC is falling, MC will fall more sharply.
- If AC is rising, MC will rise more sharply.
- MC began to rise point sooner than AC.
- MC began to rise earlier than AC.



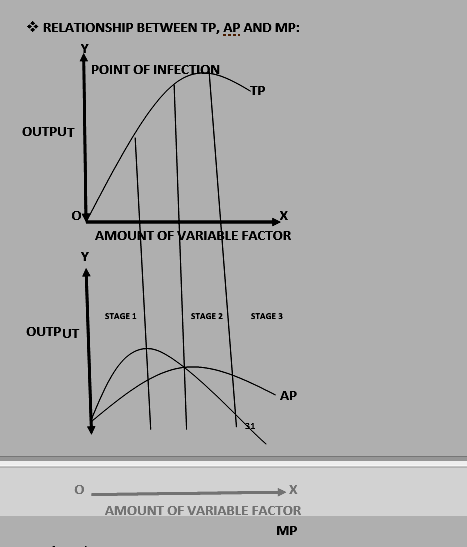
· Law of variable proportion:
It show the behavior of output as the quantity of one factor is increased, other factor remains constant, and further it depicts that AP and MP will start to decline.
· Law of return to scale:
The percentage increase in physical output when all input changes in the same percentage are known as return to scale.



A= MR=MC B= MR>MC
MC curve cuts MR from below
v Under short term period:
- Super normal profit:
- More than normal profit is super profit.
- In this case AR is more than AC.
- MC=MR (equilibrium point).
- AC curve below the MC curve (MC>AC).
B. Normal profit (short period):
- AC=AR
- MC=AC
- Normal profit is also known as zero profit because it includes in the cost of production.




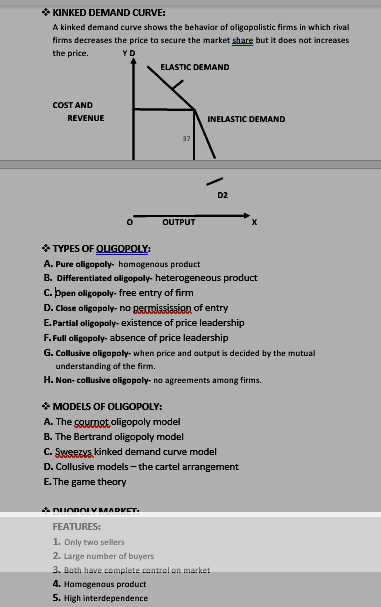
DUOPOLY MARKET: FEATURES:
1.Only two sellers
2.Large number of buyers
3.Both have complete control on market
4.Homogenous product
5.High interdependence
6.High barriers to entry
DUOPOLY MODELS:
1.Cournot model
2.Chamberlin model
3.Edge worth model
4.Stackelberg model
5.Bertrand model
MONOPSONY MARKET:
One buyer and many sellers.
PROFIT:
Gross profit= total revenue- explicit cost
Net profit= total revenue- (explicit implicit cost)
THEORIES OF PROFIT:
1.Rent theory of profit- F.A walker
2.Wage theory of profit- Daven port
3.Marginal productivity theory of profit- Chipman Stigler
4.Risk theory of profit- Prof. Hawley
5.Uncertainty theory of profit- Prof. Frank H Knight
6.Socialist theory of profit- Karl Marx in his book Das capital
7.Dynamic theory of profit-Prof. J.B. Clark
8.Innovative theory of profit- Joseph Shumpeter
IMPORTANT POINTS:
•Father of economics – Adam Smith
•Micro and Macro economics terms are introduced by – Ragner Frisch
•Concept of marginal utility analysis – Alfred Marshall
•Law of diminishing marginal utility and law of equi marginal utility- H.H.Gossen
•Demand paradox for inferior goods- Robert Giffin
•Concept of consumer surplus- Marshall
•Author of Value and Capital- J.R. Hicks
•Theory of circular causation- Ragner Nurkse
•Concept of indifference curve analysis- Hicks and Allen 1881
•Revealed preference theory- Paul Semulson
•Substitution effect- Hicks and Allen
•Scientific touch to indifference curve analysis- F.Y Edge worth
•Principle of economics- Alfred Marshall 1890
•Diamond water paradox- Adam smith
•Language of economics- J.K Galbraith
•Degree of price discrimination- A.C Pigou
•Demonstration effect- Thorsteing veblen
•Product exhaustion theorem- Clark wicksteed
•Demand schedule at different price- Catherin
•Monopsony concept- Mrs. J Robinson
•Infant industry argument- Freidrich list
•Social accounting concept- J.R Hicks 1970
•Zero based budgeting- Zimmy carter 1970
•Zero based budgeting in India- 1983
•Positive economic aspect- Robbins (Peter A Peiyar)
•Welfare definition- Marshall
•Wealth definition- Adam smith
•Population theory- Robert Malthus
•Theory of demand- Marshall
•Theory of imperfect competition- John Robinson
•Quasi rent- Marshall
•Positive science economics- Robbins
•Scarcity definition- Robbins
•Wealth of nation- Adam smith
•Growth definition- Paul samulson
•Liquidity preference theory- Keynes
•The modern theory of interest- J.R. Hicks and Hanson
•Theory of monopolistic competition- Chamberlin
•General theory of Employment, Interest and money- J.M. Keynes
•Nature and significance of economic science- Robbins.







