GOODS AND SERVICES TAX (G.S.T)
TAX –
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed upon a taxpayer by a government spending and various public expenditures.
A tax is a compulsory payment made by individuals to the govt. for welfare of our nation itself.
There are basically 2 types of taxes :
- Direct tax
- Indirect tax
DIRECT TAX –
Direct tax is a type of tax where the incidence and impact of taxation fall on the same entity.
In the case of direct tax, the burden can’t be shifted by the taxpayer to someone else. There are largely taxes on income or wealth. Income tax, corporation tax, property tax, inheritance tax and gift tax are examples of direct tax.
INDIRECT TAX –
MEANING OF INDIRECT TAX –
Indirect taxes are those taxes which have their primary burden or impact on a single person . But that person succeeds in shifting his burden to others. In other words, an indirect tax is imposed on one person but is paid partly or wholly by another.
Indirect taxes are shifted and the incidence of these taxes falls on persons other than the original payers.
DEFINITION OF INDIRECT TAX –
Indirect tax is a type of tax where the incidence and impact of taxation does not fall on the same entity.
TYPES OF INDIRECT TAX –
- Excise duty : This duty imposed by the govt. on the manufacture or production of some goods.
- Customs duty : Duties of customs were levied on goods imported or exported from India.
- Service tax : It was levied on the gross or aggregate amt. charged by the service provider from the service receiver.
- Sales tax : Tax paid by the consumer on the purchase of some items.
- VAT : It was a tax on the sale of goods. It was imposed on intra-state sale i.e., sale of goods within the state.
RIGHT TO IMPOSE INDIRECT TAX BY CENTRE/STATE & UNION TERRITORY GOVERNMENT BEFORE AND AFTER 101ST AMENDMENT OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA –
The Constitutional (101st Amendment) Bill 2016, was cleared by the parliament by early august 2016 – the way for its implementation finally, the new federal indirect tax GST was enforced by the govt. on July 1, 2017.
- To apply to all goods other than alcoholic liquor for the human consumption, petroleum crude, motor spirit, natural gas, petrol etc.
- A total of 9 taxes subsumed under it ( VAT, central sales tax, luxury tax, entry tax, entertainment tax, taxes on lotteries, state surcharged and cesses) so far as they relate to supply of goods and services.
- On inter-state transactions of goods and services on IGST will be levied.
- There are 5 slabs in GST like 5%, 12%, 18% & 28%.
- Luxury cars, pan masala, tobacco products to be classified as under 28% GST.
- Central tax before GST custom duty, services tax, central excise duty, etc.
- GST came into effect on the principle of ONE NATION ONE TAX.
- GST has been divided into 3 types CGST/UTGST, SGST, IGST.
- Taxes of centre (service tax, stamp tax, central sales tax) and taxes (excise, VAT, entry tax, lease tax, luxury tax, work contract tax, octroi, turnover tax) of the state to be merged into GST.
GOODS AND SERVICES TAX –
INTRODUCTION OF GST IN INDIA –
GST is an indirect tax used in India on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive , multistage, destination-based tax: comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except a few state taxes.
Goods and services are divided into 5 different tax slabs for collection of tax : 0%, 5% ,12%, 18% & 28% .
However, petroleum products , alcoholic drinks, and electricity are not taxed under GST and instead are taxed separately by the individual state governments, as per the previous tax system.
The tax came into effect from 1st July 2017 through the implementation of the 101ST Amendment Of The Constitution of India by the Indian govt. the GST replaced existing multiple tax levied by the central govt. and state govt.
MEANING OF GST –
GST is a value added tax levied on manufacture, sale and consumption of goods and services . It is a destination based tax on supply of goods and services , levied at all stages , right from manufacture upto final consumption with credit of tax paid on previous stages available as set-off. GST would accrue to the taxing authority which has jurisdiction over the place of supply.
SUPPLY –
CONCEPT OF SUPPLY-
GST would be applicable on supply of goods or services as against the present concept of tax on manufacture of goods or on sales of goods or on provision of the services.
It includes all sorts of activities like manufacture , sales, bartar, exchange ,transfer, etc.
It also includes supply made without consideration in certain specified situation.
THRESHOLD EXEMPTION-
Threshold limit of aggregate turnover for exemption from registration and payment of GST for the supplier could be Rs. 4000000 and Rs.
2000000(state of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Puducherry, Sikkim, Tripura, and Uttarakhand -1st April 2019 (with eefect from ).
A common threshold exemption applies to both CGST and SGST. The benefits of threshold exemption, however is not available in inter-state supply of goods.
GST COUNCIL-
As provide for an article 279(A) of the constitution, the GST council was notified with effect from 12 Sep. 2016. The council is chaired by the union finance minister, the minister of state (revenue and the state finance minister as member). It shall made recommendations to the union and the state on the following issues-
- The taxes, sales and such charges levied by the centre, the state and the local bodies which may be subsumed under GST.
- The goods and services that may be subjected to or exempted decided by council.
- Modern GST laws – principles of levy, ratio of IGST and the principle that governed the place of supply.
- The threshold limit of turnover below which the goods and services may be exempted from IGST.
- The rates including floor rates with bands of GST.
- Any special rate for specified period to raise additional resource during any natural calamities or disasters.
- Special provision with respect to north-east states, J&K, Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand .
- Any other matter related to GST as the council may decide.
The council shall recommended the date on which the GST be levied on petroleum crude, high speed diesel, natural gas, aviation turmine tube.
While discharging the function confirmed by article, the GST Council shall be guided by the need for various structure of goods and services tax and tax for the development of various national market for goods and services.
On half of the total no. of member of GST Council shall constitute the quorum. GST council shall determine the procedure in the performance of its function . every decision of GST council shall be taken in a meeting.
By majority not less than 3/4th of the weighted boards of the members present and voting , in accordance with the principle:
- The vote of central govt. shall have the weightage of 1/3rd of the total votes caste.
- The vote of all the state govt. taken together shall have a weightage of 2/3rd of the total vote caste in that meeting.
The council has made for 34th times & no occasion has arisen so far that required.
LEGAL /RULES –
- Recommending GST laws. (CGST Law, UTGST Law, IGST Law, SGST Law).
- Rules on composition, registration, input tax credit, invoice, determination of value of supply, accounts and records, returns, payment, refund, assessment and audit, advance ruling, appeals and revisions, anti-profitory, tradition provisions, e-way bills, inspection, search-scizor, demands and recoveries and oftens and penalities have been recommended.
PERSON-
A taxable person under GST, is a person who carries on any business at any place in India and who is registered or required to be registered under the GSTact.
Any person who engages in economic activity including trade and commerce is treated as taxable person.
Person here includes individuals, HUF, company, firm, LLP and any corporation or govt. companies, body corporate incorporated under laws of foreign country, co-operative society, local authority, govt., trust, artificial juridicial person.
Person is defined under Section 2(84) of CGST Act, 2017.
Anybody incorporated by or under the laws of a country outside India is also a person under GST law.
BUSINESS-
The GST is a value added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption . The GST is paid by the consumers, but it is remitted to the govt. by the businesses selling the goods and services.
The new GST law grants a basic exemption of Rs. 20lacs to small business owners. Suppliers shall not be liable for GST if their aggregate turnover in a financial yr. doesn’t owed Rs. 20lacs.
Small businesses will see a big transformation of the taxation system once the goods and services tax arrives. Moreover, the new proposed system (from July 2017) will be more transparent and paperless but requires more compliances as well.
However , any business whose turnover exceeds Rs. 40lacs in a financial yr. is required to register under GST. This limit is Rs. 20lacs for service providers.
This higher threshold under GST has brought compliance relief to many small businesses , including startups in India.
Earlier, to start business many different tax applications were required, but under GST regime, only GST registration is sufficient for all compliances.
APPROPRIATE GOVERNMENT –
As per section 2(53) of the CGST Act,2017 , govt. means the central govt.
As per clause (23) of section 3 of the general clause act, 1897 the govt. includes both the central govt. and state govt.
In terms of article 77 of the constitution, all executives actions of the govt. of India shall be expresses to be taken in the name of the president
.
Therefore, the central govt. means the president and the officers subordinate to him while exercising the executives powers of the union vested in the president and in the name of the president.
MIXED SUPPLY-
Two or more individual suppliers of goods and services or any combinations thereof made in conjuction with each other by a taxable person for a single price where such supply doesn’t constitute a composite supply.
A supply of a package consisting of chocolates, sweets, cakes, dry fruits, etc. when supplied for a single price is a mixed supply. Hence , each of the items can be supplied separately and is not dependent on any other.
Example-
- Supply of toothpaste with toothbrush.
- A gift pack comprising of chocolates and sweets.
COMPOSITE SUPPLY –
A supply made by a taxable person to a recipient comprising two or more supplies of goods and services or any combination thereof which are naturally bundled ans supplied in conjuction with each other in the ordinary course of business, one of which is a principal supply.
Where goods are packed and transported with insurance, the supply of goods, packing materials, transport and insurance is a composite supply and supply of goods is the principal supply.
Example-
- Supply of AC and installation of the same.
- Education services along with supply of study material.
GSTN-
Goods and services tax network.
GSTN has been incorporated on 28th march, 2013 under section 25 of the companies act, 1956, not for profit as non-government, private limited company similar to section 8 of companies act, 2013.
GSTN has been set-up primarily to provide IT infrastructure and services to the central and state govt. , taxpayers and other stakeholders for the implementation of the GST in India.
FUNCTIONS OF GSTN-
- Facilitating registration.
- Forwarding returns to central and state authorities.
- Computation and settlement of IGST.
- Matching of tax payment details with banking network.
- Providing analysis of taxpayers.
GSTN is developing a common GST portal and applications for registration, payment, returns and MIS reports. It is developing back-end modules like assessment, audit, refund, appeal, etc.
GSTIN-
Goods and services tax identification number).
All the business entities registering under GST will be provided a unique identification no. known as goods and services tax identification no.
Under GST regime, the different identification no. has been replaced by single type of registration no. for everyone (GSTIN) . This will ensure better administration by the authority and greater compliance by taxpayers and hopefully improve tax collection.
Where,
22- State code
FORMAT OF GSTIN-
22 AAAAA0000A 1 Z 5
AAAAA0000A- Permanent account number (PAN) 1-Entity no. of the same PAN holder in a state
Z –By default
5- Check sum digit used for detection of errors
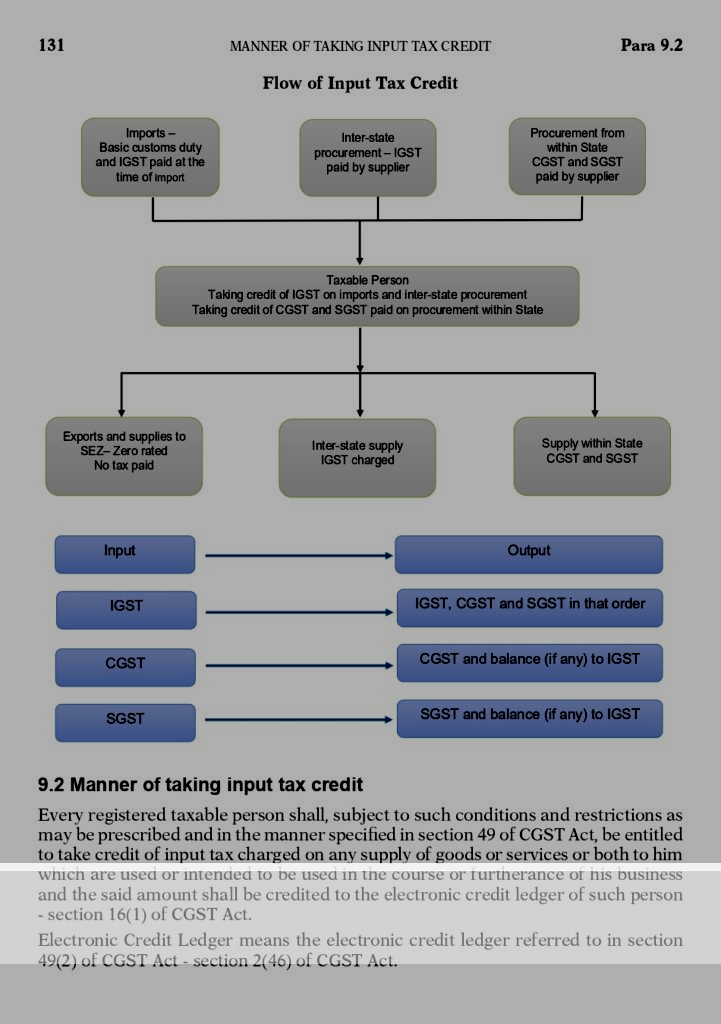
E-C OMMERCE INPUT TAX CREDIT-
Input tax credit mechanism and e-commerce seller can avail input tax credit.
Input tax credit means at the time of paying tax on output, you can reduce the tax you have already paid on inputs.
GST MODELS
SINGLE GST-
Single rate GST means one tax rates which levied on supply of goods or services.
But in India it is difficult to maintain single tax rate for all supply of goods or services due to diversity of people, states, goods etc.
So govt. opted for 4 slabs for both goods and services- 5%, 12%,18%, 28%.
DUAL GST-
The dual GST is assumed to be a simple tax with one or two central goods and services tax (CGST) and state goods and services tax (SGST) rates.
In India, both centre and state have been assigned the powers to levy and collect taxes through appropriate legislation. Both the centre centre and state govt. have distinct responsibilities to perform acc. To the division of powers as prescribed in the constitution that needs resources for implementation. A dual GST is therefore, is appropriately aligned with the constitutional requirement of fiscal federalism.
TYPES OF GST-
CGST –
CGST stands for Central goods and services tax.
Central goods and services tax subsumed all the taxes levied by the central govt.
They are levied by the central govt. for intrastate movement of goods and services. Intrastate means within one state.
For example : Central excise duty, central surcharges and cess and other such central indirect taxes that were earlier applicable.
SGST –
State goods and services tax or (SGST) subsumed all taxes levied by the state govt., that’s state indirect taxes.
For example : VAT, sales tax, state cesses and surcharges, etc.
IGST –
Integrated goods and services tax or (IGST) levied on interstate movement of goods and services.
LEVY OF GST –
Levy of tax means the imposition of taxes as well as assessment of tax but it does not include collection of tax. In other words, the levy of GST means imposition of GST and then determining the amount of tax.
COLLECTION OF GST –
Collection of tax means the point of time for payment of tax. Though liability to pay tax arises as soon as Taxable Event occurs but for administrative convenience, tax is collected monthly or quarterly. So that assessee need not to file return and pay tax every time as and when taxable event takes place.
Thus, levy of tax is the stage when tax is imposed, but collection is the stage when tax is actually realized.
- GST model followed by India – Canada model
- Chairperson of GST Council – Union Finance Minister (NIRMALA SITHARAMAN)
Need for registration: Registration under GST law provides the following benefits:
•If turnover of the person exceeds the threshold limit, registration is the mandatory requirement.
•It legally recognizes a person as supplier of goods and/or services.
•It authorizes collection of GST from customers.
•It allows claim of input tax credit of GST paid on purchases of goods and services and utilizing the same for payment of taxes due on supply of goods and services.
•It allows us seamless credit of the input tax from the manufacturer/imported to the last supplier in the claim.
•Proper accounting of taxes paid on the input goods and services. Registration is mandatory for:
•Casual taxable person.
•Non-resident taxable person.
•Agents of a supplier.
•Text pairs paying tax under reverse charge mechanism.
•Input service distributor.
•E-commerce operator for aggregator and their suppliers.
•Person supplying online information and database access or retrieval services from a place outside India to a person in India, other than a registered taxable person
Who is not liable to take registration?
The person is not liable for registration if he is:
1.Engage exclusively, in the business of supplying goods and services that are either not liable to tax; or are wholly exempt from tax under GST laws.
2.An agriculturalist, to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land.
Therefore, if the agriculturist is engaged inBthe business of goods, which are not produce out of cultivation of land e.g. dairy farming, sericulture, stock breeding etc., he shall be required to register under the GST laws.
3.The government may, buy notification specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining the registration.
Mandatory registration: Every supplier shall be liable to be registered in the state/UT from where he made a taxable supply of goods or services or both if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds the threshold limit of rupees 20 lakh.
Aggregate turnover
“aggregate turnover” for a person having the same PAN, to be computed on all
India basis, is aggregate value of:
I- All taxable supplies
II- Exempt supplies including non- taxable supplies
III – Exports of goods and/or services
IV- Inter- State supplies
V- supply of goods, after completion of job work, bi a registered job worker to be treated as a supply of goods by the “principal”, and The value of such goods not to be included in the aggregate turnover of the registered job worker.
Registration in each state: Person having same PAN is operating Every person, who is liable to take a registration, shall obtain registration separately for each of the states, wherever he has place of business and is liable to pay GST.
Deemed registration
Registration under GST is not text specific, which means that there is a single registration for all the taxes i.e. CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST and cesses.
Voluntary registration
1.Any person, who is not liable to obtain registration mandatorily, main registered voluntarily. All provisions of GST law as are applicable to the registered person shall be applicable after registration.
2.The proper officer may, in the prescribed manner cancel the registration of taxable person who has taken voluntary registration and has not commenced business within six months from the date of registration.
3.However, no application for cancellation of registration shall be considered in case of taxable person who has been registered voluntarily before the expiry of a period of one year from the effective date of registration.
Who is a casual taxable person?
if you occasionally make supply of goods or services as a principal or agent or any other capacity in taxable territory, where GST applies but where you don’t have a fixed place of business. As per GST, you will be treated as a casual taxable person.
Who is a non – resident taxable person?
Non – resident is a taxable person residing outside India and coming to India to officially undertake transaction whether as principal, agent or in any other capacity, but has no fixed place of business in India. He shall apply for registration at least 5 days prior to the commencement of business.
For job worker: GST law does not prescribe any search condition for compulsory registration for job worker. However, since she is also a service provider, he shall
BBrequire registration at the time when his aggregate turnover exceeds the threshold limit.
Long answer type questions:
1.What are the benefits of registration under GST? What are the types of registration under GST? Explain in details.
2.Under what circumstances registration under GST not required? Short answer type questions:
Write short notes on:
a-Need of Registration under GST
b-Aggregate turnover for registration c- Voluntary registration
d- Casual and non – resident taxable person.
Reverse Charge Mechanism
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
1.The Central goods and services tax (CGST) shall be levied on all intra-State supplies of goods or services or both, except on the supply of alcoholic liquor for human consumption, on the value determined under section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017.
2.The Central tax
on the supply of
petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas and aviation turbine fuel
shall be levied with effect from such date
as may be notified by the Government
on the recommendations of the Council
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
3.Reverse Charge
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification,
specify categories of supply of goods or services or both,
the tax on which shall be paid
on reverse charge basis by the recipient of such goods or services or both and
all the provisions of CGST Act
shall apply to such recipient as
if he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such goods or services or both
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
4.Registered persons, liable to pay tax on reverse charge basis
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification,
specify a class of registered persons
who shall, in respect of supply of specified categories of goods or services or both
received from an unregistered supplier,
pay the tax on reverse charge basis as the recipient of such supply of goods or services or both, and
all the provisions of CGST Act
shall apply to such recipient as
if he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to such supply of goods or services or both.
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
5.The electronic commerce operator
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification,
specify categories of services,
the tax on inter-State supplies of which
shall be paid by the electronic commerce operator
if such services are supplied through it, and
all the provisions of this Act shall apply to such electronic commerce operator as
if he is the supplier liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such services.
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
5.The electronic commerce operator- not have physical presence
an electronic commerce operator
does not have a physical presence in the taxable territory,
any person representing such electronic commerce operator
for any purpose in the taxable territory
shall be liable to pay tax.
Levy and Collection of CGST
According to Sec. 9 of CGST Act, 2017-
5.The electronic commerce operator- not have physical presence and also not have a representative in the said territory
an electronic commerce operator
does not have a physical presence in the taxable territory,
and also does not have a representative in the said territory
such electronic commerce operator shall
point a person in the taxable territory
for the purpose of paying tax and
such person shall be liable to pay tax.
Composition Scheme under GST
Need to Introduce GST Composition Scheme:
Composition scheme under the law is for small businesses. This is to bring relief to small businesses so that they need not be burdened with the compliance provisions under the law. Thus, an option has been provided where they can opt to pay a fixed percentage of turnover as fees in lieu of tax and be relieved from the detailed compliance of the provisions of law.
Conditions for Opting for Composition
Scheme under GST: Sec 10
•The person opting for composition levy should be a registered person.
•A taxpayer whose turnover is below Rs 1.5 Crore can opt in for Composition Scheme. In case of special states the limit is Rs 75 lakhs.
•No Input Tax Credit can be claimed by a dealer opting for compositionscheme
•The taxpayer can only make intra-state supply (sell in the same state) i.e. no inter-state supply of goods
•The dealer cannot supply GST exempted goods
Main points of Composition Scheme
•Registration: can select composition plan or general plan.
•Eligibility: whose turnover in Previous F.Y is upto 1.5 crore and in 75 lakhs in special states.
•Special states: Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, Tripura, Sikkim, Uttrakhand Persons would not be entitled to opt for Composition Levy
•Supplier of services other than restaurant related services
•Manufacturer of ice cream, pan masala, or tobacco
•Casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person
•Businesses which supply goods through an ecommerce operator
•Tax payers who make tax-free supplies only
•Tax payers supplying interstate
What is Zero Rated Supply?
GST is not applicable in India for exports. Hence, all export supplies of a taxpayer registered under GST would be classified as a zero-rated supply. According to Section 16 of the IGST Act, zero-rated supply means any of the following supplies of goods or services:
Export of goods or services or both;
Supply of goods or services or both to a Special Economic Zone developer
Supply of goods or services or both to a Special Economic Zone unit. GST Refund for Zero Rated Supply
As per GST rules, the supplier can claim the input tax credit in respect of goods or services used for the supplies as exports act as zero-rated supply, even though termed as non-taxable or even exempt supplies.
To claim GST refund for exports, the taxpayer can export under bond or LU and claim refund or export on payment of IGST and claim a refund.
Supplied Exempt from GST
Exempt supply under GST
Exempt supply under GST means supplies which not attract goods and service tax. In these supply no GST is charged. Input tax credit paid on these supplies will not be able for utilization. supply which are considered as exempt supply:-
•supplies which are chargeable to nil rate tax.
•supplies which are partially and wholly exempt from the charge of GST.
•supplies which are not taxable under the Act like alcoholic liquor for human consumption.
GST exemptions for goods
There is a list of goods which do not attract GST as recommended by the GST Council. The reasons for granting exemption on goods might include any of the following –
•In the interest of the public
•The exemption is as per the GST Council’s recommendation
•The exemption is granted by the Government through a special order
•The exemption is allowed on specific goods through an official notification
Type of Exemption
•Absolute exemption: when exemption given exclusively. Ex. Electricity
distribution, services of RBI
•Conditional exemption: when certain conditions are applied for exemption and
the exemption is granted only after the fulfillment of those condition.
•Threshold limit exemption
•Geographical exemption
•Exemption for specific goods and services: largely used consumer goods &
services
•Exemption for non-taxable supplies: items outside GST regime


Types of GST Returns
- GSTR-1
GSTR-1 is the return to be furnished for reporting details of all outward supplies of goods and services made, or in other words, sales transactions made during a tax period, and also for reporting debit and credit notes issued. Any amendments to sales invoices made, even pertaining to previous tax periods, should be reported in the GSTR-1 return.
GSTR-1 is to be filed by all normal taxpayers who are registered under GST. It is to be filed monthly, except in the case of small taxpayers with turnover up to Rs.1.5 crore in the previous financial year, who can file the same on a quarterly basis.
2. GSTR-2A
GSTR-2A is the return containing details of all inward supplies of goods and services i.e. purchases made from registered suppliers during a tax period. The data is auto-populated based on data filed by the suppliers
in their GSTR-1 return. GSTR-2A is a read-only return and no action can be taken.
3. GSTR-2
GSTR-2 is the return for reporting the inward supplies of goods and services i.e. the purchases made during a tax period. The details in the GSTR-2 return are auto- populated from the GSTR-2A. Unlike GSTR-2A, the GSTR-2 return can be edited.
GSTR-2 is to be filed by all normal taxpayers registered under GST, however, the filing of the same has been suspended ever since the inception of GST.
4. GSTR-3
GSTR-3 is a monthly summary return for furnishing summarized details of all outward supplies made, inward supplies received and input tax credit claimed, along with details of the tax liability and taxes paid.
This return is auto-generated on the basis of the GSTR- 1 and GSTR-2 returns filed.
GSTR-3 is to be filed by all normal taxpayers registered under GST, however, the filing of the same has been suspended ever since the inception of GST.
5. GSTR-3B
GSTR-3B is a monthly self-declaration to be filed, for furnishing summarized details of all outward supplies made, input tax credit claimed, tax liability ascertained and taxes paid.
GSTR-3B is to be filed by all normal taxpayers registered under GST.
6. GSTR-4 / CMP-08
GSTR-4 is the return that was to be filed by taxpayers who have opted for the Composition Scheme under GST. CMP-08 is the return which has replaced the now erstwhile GSTR-4. The Composition Scheme is a scheme in which taxpayers with turnover up to Rs.1.5 crores can opt into and pay taxes at a fixed rate on the turnover declared.
The CMP-08 return is to be filed on a quarterly basis.
7. GSTR-5
GSTR-5 is the return to be filed by non-resident foreign taxpayers, who are registered under GST and carry out business transactions in India. The return contains details of all outward supplies made, inward supplies received, credit/debit notes, tax liability and taxes paid.
The GSTR-5 return is to be filed monthly for each month that the taxpayer is registered under GST in India.
8. GSTR-6
GSTR-6 is a monthly return to be filed by an Input Service Distributor (ISD). It will contain details of input tax credit received and distributed by the ISD. It will further contain details of all documents issued for the
distribution of input credit and the manner of distribution.
9. GSTR-7
GSTR-7 is a monthly return to be filed by persons required to deduct TDS (Tax deducted at source) under GST. GSTR 7 will contain details of TDS deducted, the TDS liability payable and paid and TDS refund claimed, if any.
10. GSTR-8
GSTR-8 is a monthly return to be filed by e-commerce operators registered under the GST who are required to collect tax at source (TCS). GSTR-8 will contain details of all supplies made through the E-commerce platform, and the TCS collected on the same.
The GSTR-8 return is to be filed on a monthly basis.
11. GSTR-9
GSTR-9 is the annual return to be filed by taxpayers registered under GST. It will contain details of all outward supplies made, inward supplies received during the relevant previous year under different tax heads i.e. CGST, SGST & IGST and HSN codes, along with details of taxes payable and paid. It is a consolidation of all the monthly or quarterly returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-2A, GSTR-3B) filed during that year.
GSTR-9 is required to be filed by all taxpayers registered under GST*, except taxpayers who have opted for the Composition Scheme, Casual Taxable Persons, Input Service Distributors, Non-resident Taxable Persons and persons paying TDS under section 51 of CGST Act.
*The 37th GST Council meeting took the decision to make GSTR-9 filing optional for businesses with turnover up to Rs.2 crore in FY 17-18 and FY 18-19.
12. GSTR-9A
GSTR-9A is the annual return to be filed by taxpayers who have registered under the Composition Scheme in a financial year*. It is a consolidation of all the quarterly returns filed during that financial year.
*GSTR-9A filing for Composition taxpayers has been waived off for FY 2017-18 and FY 2018-19 as per the decision taken in the 27th GST Council meeting.
13. GSTR-9C
GSTR-9C is the reconciliation statement to be filed by all taxpayers registered under GST whose turnover exceeds Rs.2 crore in a financial year. The registered person has to get their books of accounts audited by a Chartered/Cost Accountant. The statement of reconciliation is between these audited financial statements of the taxpayer and the annual return GSTR-9 that has been filed.
GSTR-9C is to be filed for every GSTIN, hence,
one PAN can have multiple GSTR-9C forms being filed.
14. GSTR-10
GSTR-10 is to be filed by a taxable person whose registered has been cancelled or surrendered. This return is also called a final return and has to be filed within 3 months from the date of cancellation or cancellation order, whichever is earlier.
15. GSTR-11
GSTR-11 is the return to be filed by persons who have been issued a Unique Identity Number(UIN) in order to get a refund under GST for the goods and services purchased by them in India. UIN is a classification made for foreign diplomatic missions and embassies not liable to tax in India, for the purpose of getting a refund of taxes. GSTR-11 will contain details of inward supplies received and refund claimed.